Case Study
Empowering Agentic Engineering
Powering the Next-Gen Dev Lifecycle with Jules & Azguards Technolabs

Project Summary
Azguards Technolabs engineered a high-performance integration of Jules, Google’s autonomous coding agent, into a production-ready development ecosystem. Moving beyond simple AI chat interfaces, our team built a persistent, state-aware platform where AI functions as a collaborative “Digital Engineer,” capable of navigating complex codebases, executing multi-file refactors, and maintaining project-specific context over long-term sessions.
Project Goal
The primary objective was to transition from “Human-led, AI-assisted” coding to a truly Agentic Workflow. We aimed to empower engineering teams to delegate complex, time-consuming tasks—such as performance bottlenecks and architectural refactoring—to an autonomous agent while maintaining rigorous security guardrails and human oversight.
Key Features
- Persistent Agentic Sessions
- The "Async Handshake"
- Human-in-the-Loop Governance
- Multi-Tenant Collaboration
- Automated PR Delivery
Technology Used
FastAPI
Google Jules
GitHub
PostgreSQL
SQLAlchemy
The Architecture of an Agent
Integrating an autonomous agent requires more than a simple API call. The Azguards engineering team developed a specialized three-tier architecture to handle the unpredictability of AI-driven development.

1. Session-Based State Machine
At the heart of our solution is the JulesSession model. Unlike ephemeral chat windows, our sessions are persistent “living” environments. We link the agent to specific goals, GitHub branches, and historical context, allowing a developer to pick up exactly where the agent left off, even after a hiatus.

Transparent Activity Ledger
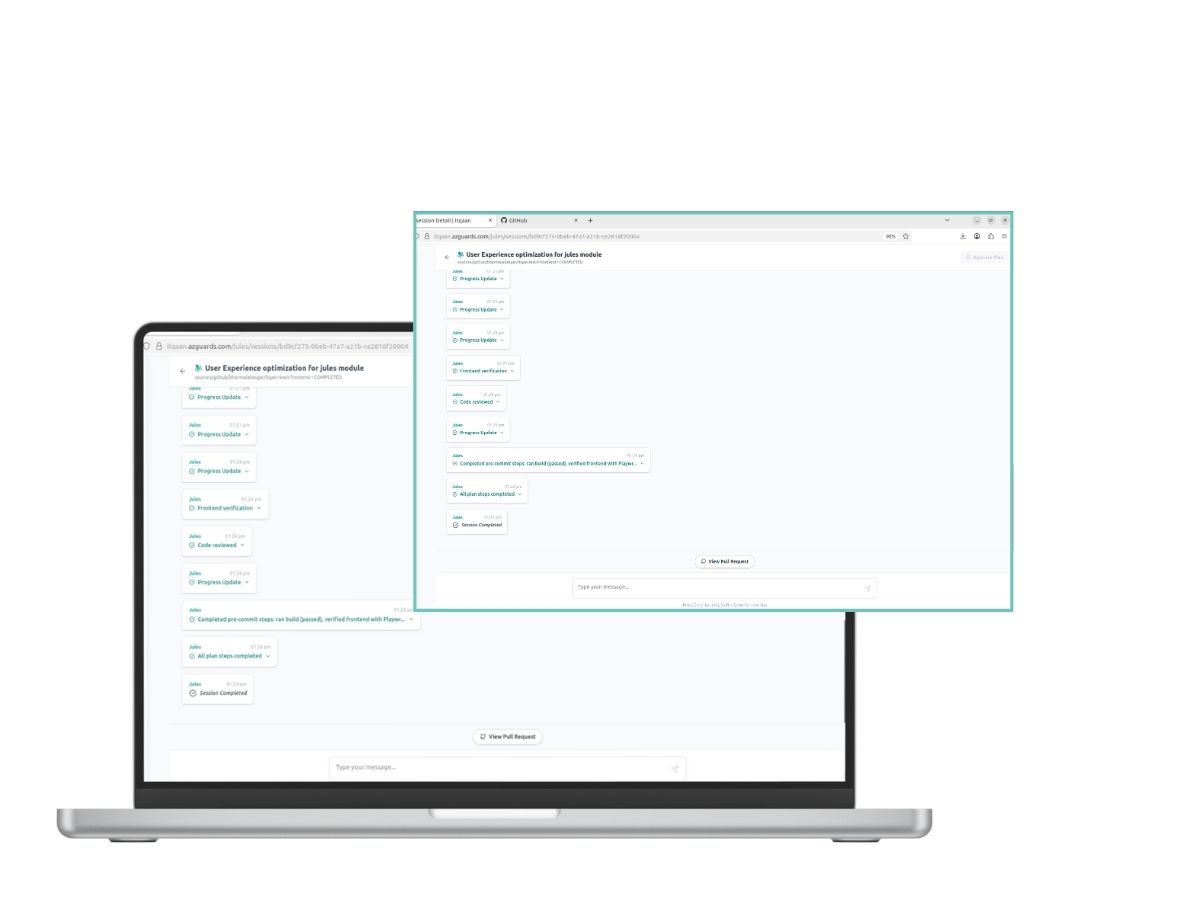
We implemented a JulesActivity stream that acts as a technical ledger. It captures the agent’s “chain of thought” rather than just the final output. This transparency allows our developers to audit the reasoning behind a code change, building trust in the autonomous system.

Optimized Asynchronous Syncing
AI agents often take minutes to process complex logic. To prevent UI lag, we built an Async Handshake protocol using FastAPI. This allows the system to record a prompt instantly, perform the heavy lifting in the background, and synchronize the results via optimized polling, ensuring a snappy, responsive user experience.
The Workflow: "Fixing Redis Performance"
To illustrate the power of this workflow, here is a walkthrough of how the Azguards team handles a real-world scenario:
Phase 1: Initiation and Context Setting
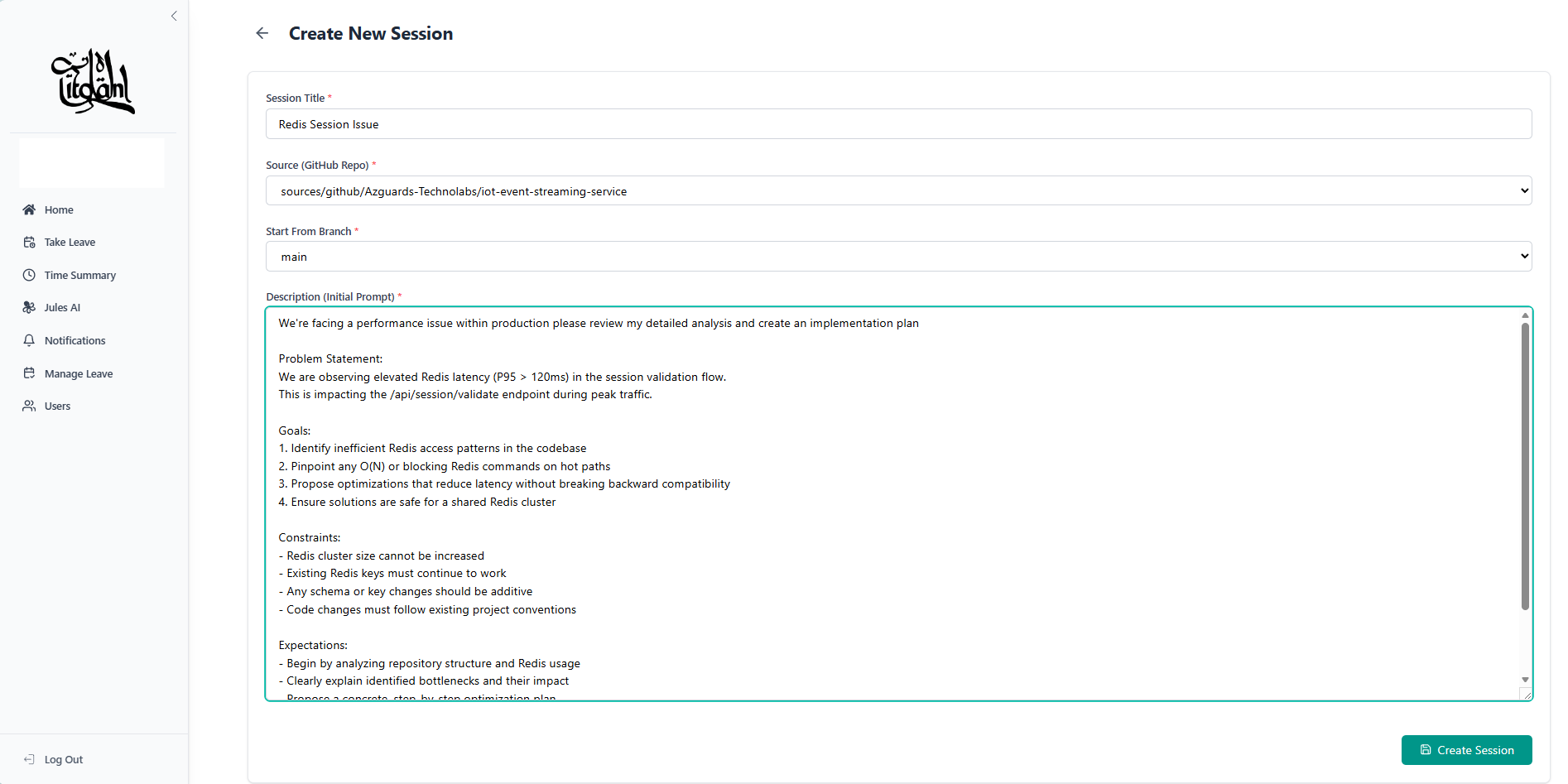
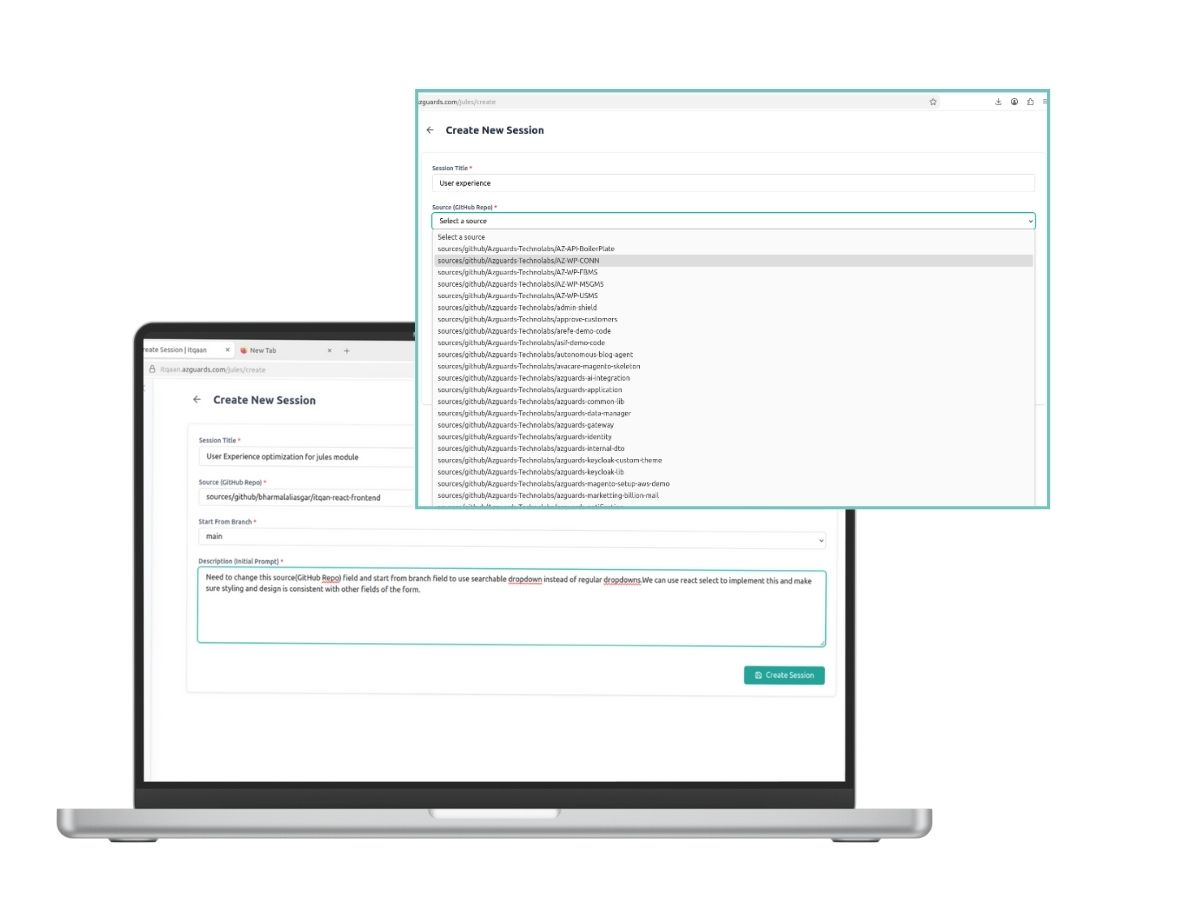
The workflow begins with a Technical Lead who identifies the problem. The Lead queries the system to select the target repository and creates a session with a specific goal, such as optimizing Redis latency. The system creates an active session linked to the main branch.
Phase 2: The Collaborative Loop
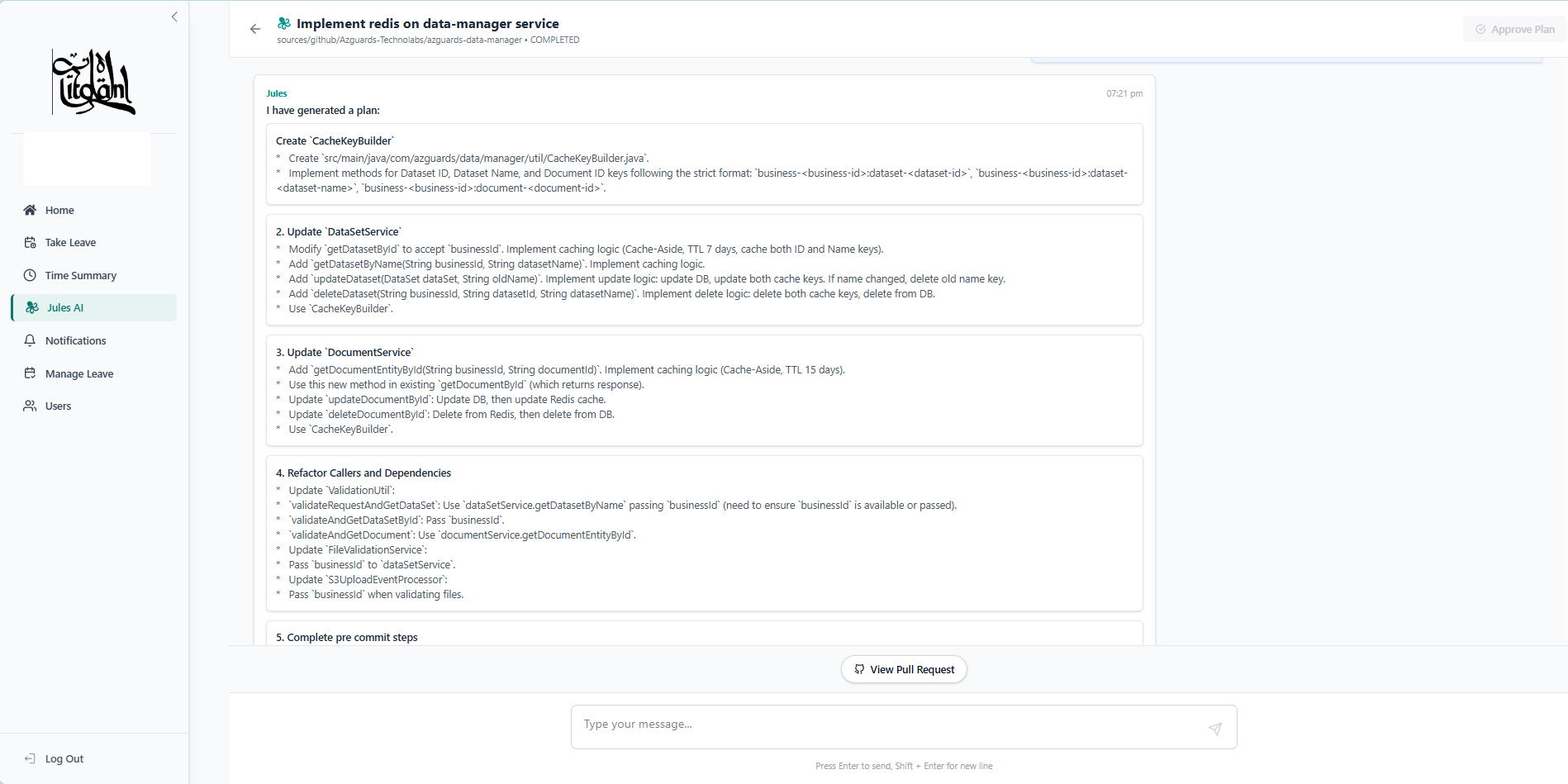
The workflow begins with a Technical Lead who identifies the problem. The Lead queries the system to select the target repository and creates a session with a specific goal, such as optimizing Redis latency. The system creates an active session linked to the main branch.
Phase 3: Plan Approval and Execution
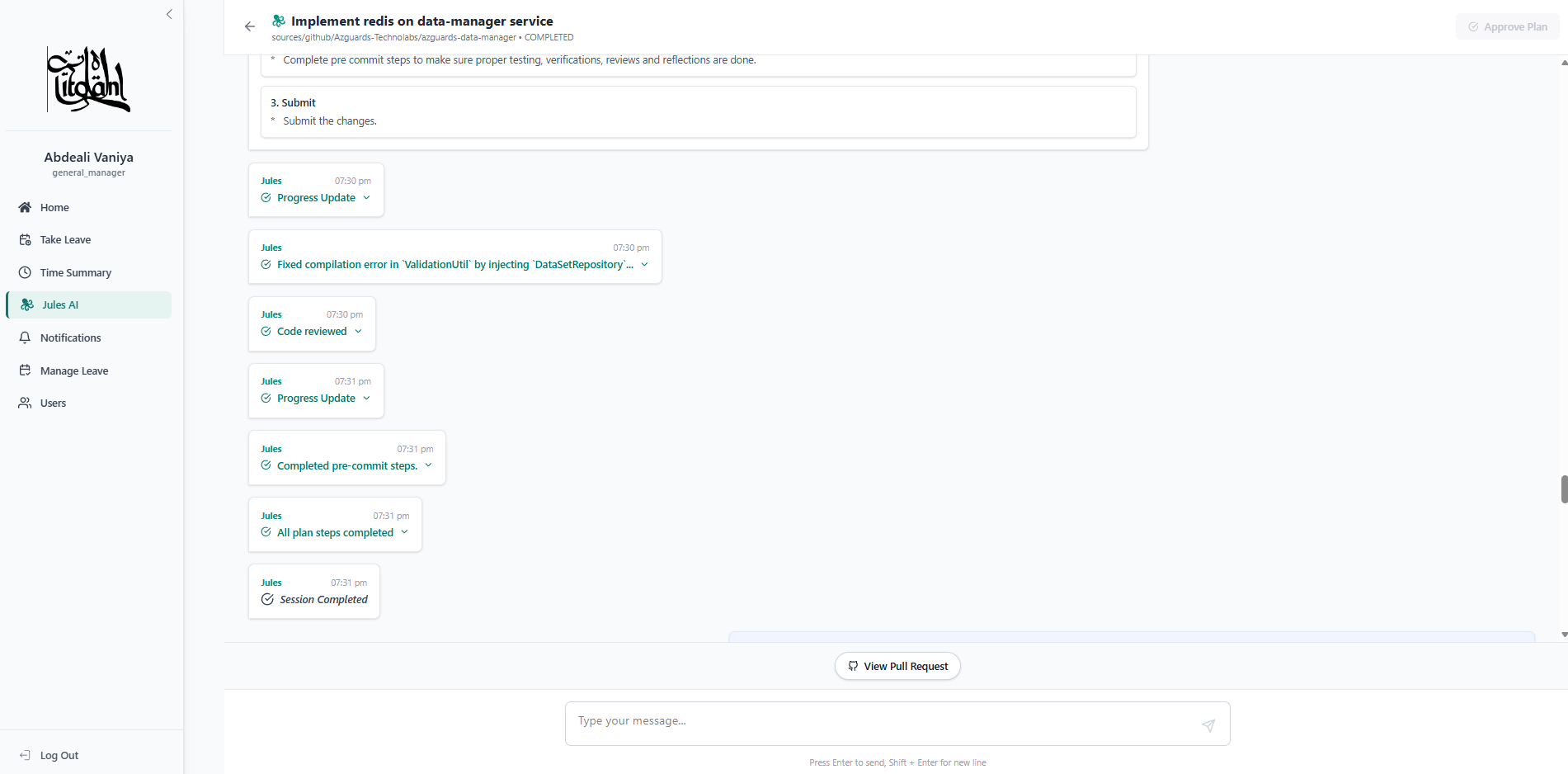
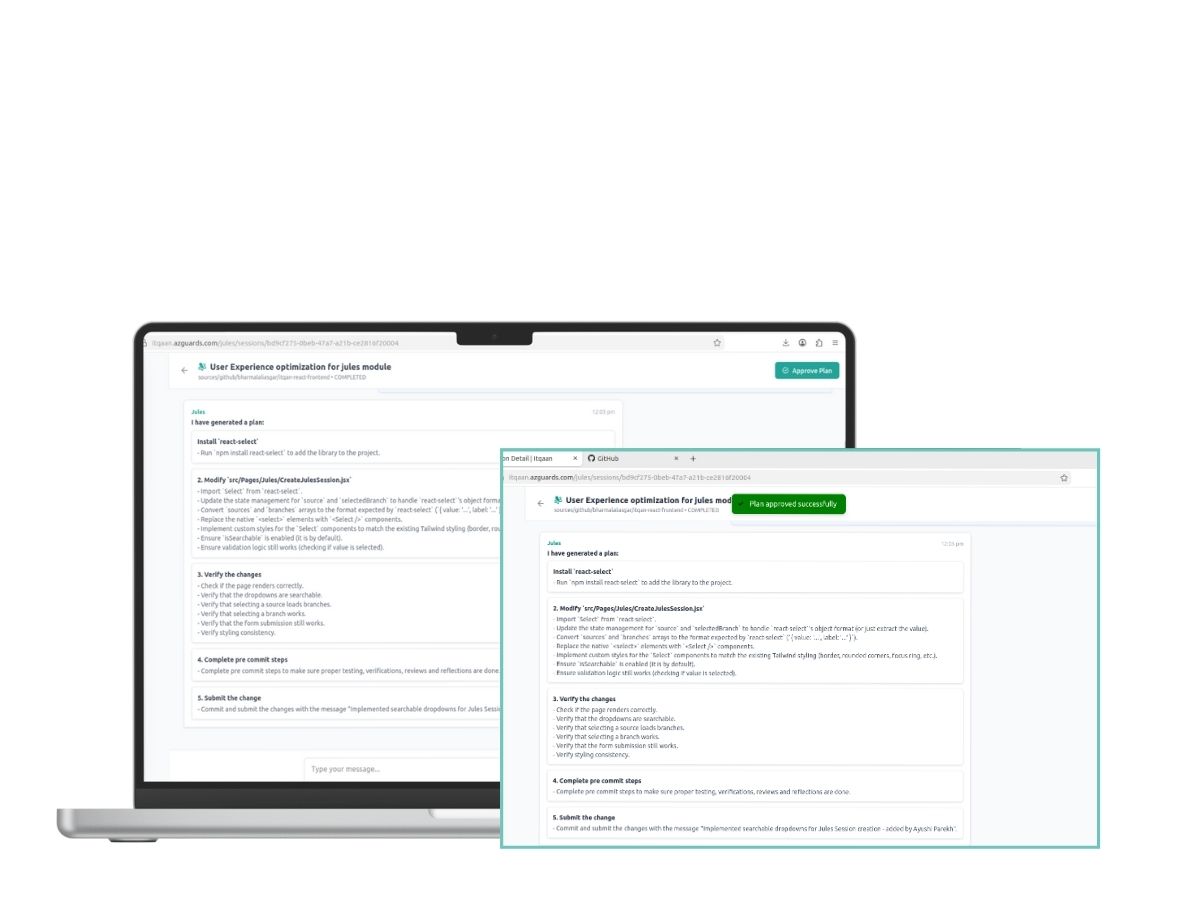
Once the approach is agreed upon, Jules proposes a concrete plan. The developer triggers the approval endpoint—a critical “human-in-the-loop” gate. This signals that the agent is authorized to generate code artifacts.
Phase 4: Artifact Generation and Delivery
Jules generates the code. The Azguards integration then automatically:
- Creates a new feature branch.
- Commits the changes with a descriptive, team-attributed message.
- Opens a Pull Request and links it back to the session for final merge.
Technical Challenges & Solutions
Challenge 1
Security & Guardrails
Giving an AI permission to write code is risky. We mitigated this by enforcing a comprehensive Guardrails strategy:
Solutions
- Global Security Policy: Jules is strictly prohibited from pushing to the main or accessing secrets.
- Branch Sandboxing: All changes happen in isolated jules/* branches.
- Project-Specific Context: We utilize AGENTS.md files within repositories to enforce unique coding standards and architectural patterns for every project.
Challenge 1
Context & Collaboration
Large repositories often exceed standard AI context windows.
Solutions
We solved this by using Summarization of large artifacts and Pagination of activity streams. Furthermore, our multi-user visibility model ensures that while a session is created by one person, it is visible and auditable by the entire engineering squad.
The Outcome
The Jules integration delivered tangible, production-grade results across engineering velocity, code quality, and team efficiency. What began as an experimental agentic workflow quickly translated into measurable gains for real-world development teams.
faster resolution of complex engineering tasks
PRs auto-generated with correct branching and commit standards
direct writes to main branch (full security compliance)
persistent session per task with long-term contextual memory

