RAG vs. Fine-Tuning: Choosing the Right Approach for Your AI Project
Large language models have become indispensable tools for businesses but using them effectively requires more than just prompting. Two dominant strategies have emerged to enhance LLM performance: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and fine-tuning. Both approaches aim to make general-purpose models more useful and domain-specific, but they work in fundamentally different ways.
Given your background in building AI-powered eCommerce solutions, understanding when and how to use each or even combine them, is critical to delivering efficient, scalable systems. This blog explores the key differences, advantages, drawbacks, and practical applications of each approach.
Understanding the Fundamentals
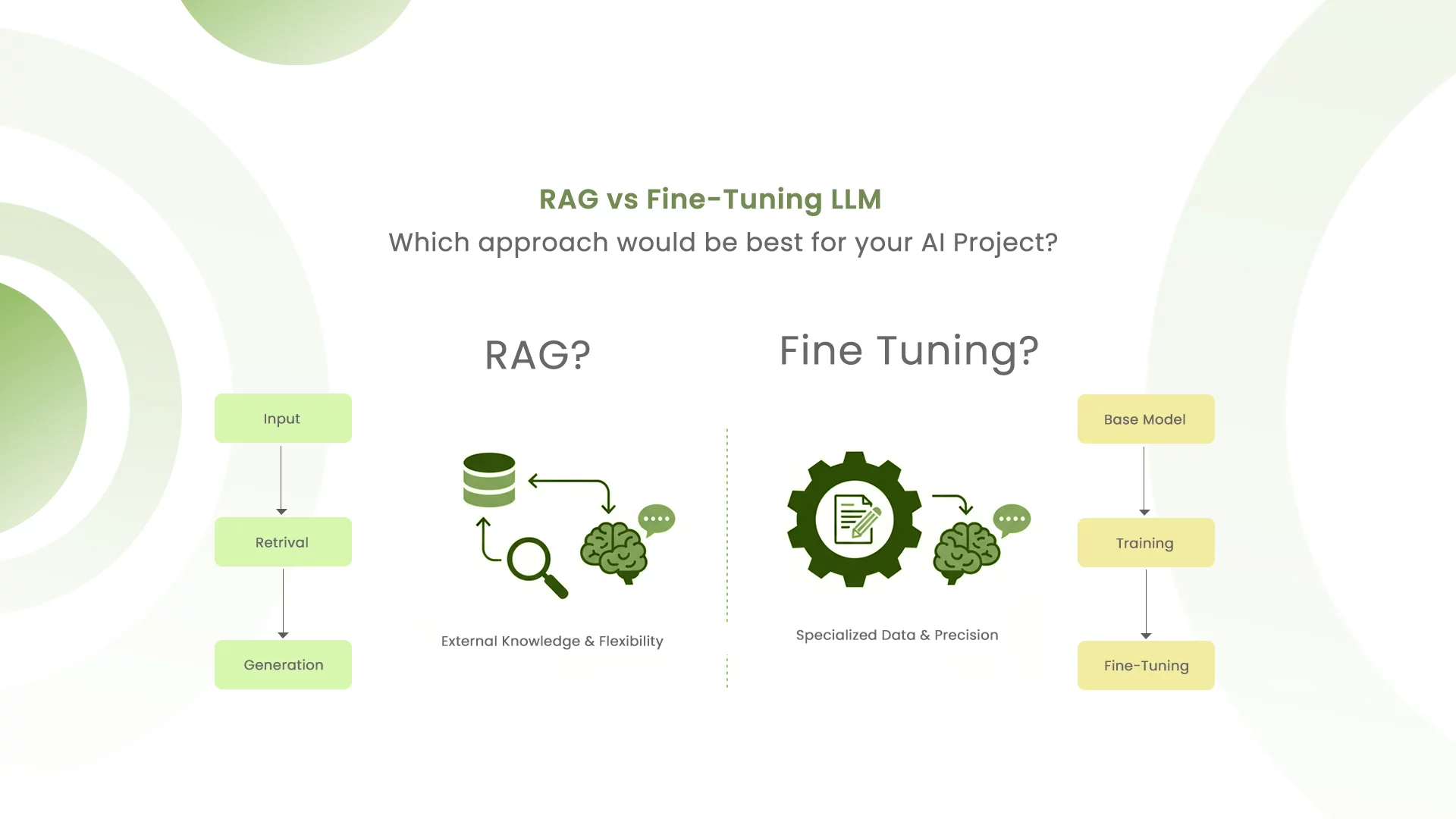
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
RAG is a technique that enhances an LLM’s responses by connecting it to external data sources in real-time. Instead of relying solely on knowledge from its training data, a RAG system follows a three-step process
- Retrieval: When a user asks a question, the system retrieves relevant information from external sources like company documents, product databases, or knowledge bases.
- Augmentation: This retrieved information is added to the prompt, providing the LLM with current, specific context.
- Generation: The LLM generates a response grounded in the retrieved data.
Think of RAG as giving your LLM access to an open book during an exam. It can pull the most relevant information on demand without needing to memorize everything.
What is Fine-Tuning?
Fine-tuning is the process of taking a pre-trained LLM and retraining it on a smaller, domain-specific dataset to adapt its behavior and improve performance on specific tasks.
Unlike RAG, fine-tuning modifies the model’s internal parameters essentially teaching it to think in a particular way Fine-tuning is like teaching the model to understand the nuances of your domain deeply. Once complete, the model “knows” your domain without needing external reference materials.
Ever thought of having your own AI Agent?
Head-to-Head Comparison
| Aspect | RAG | Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Source | External: Real-time data, documents, databases | Internal: Static knowledge frozen in model weights |
| Retraining Required | No — just update your knowledge base | Yes — requires computational retraining |
| Latency | Higher (retrieval adds overhead) | Lower (single-pass generation) |
| Cost | Lower upfront; runtime infrastructure costs | Higher upfront; GPU-intensive training |
| Data Freshness | Always current | Can become outdated; requires retraining |
| Customization | Limited to retrieval quality | Deep domain adaptation possible |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate; requires indexing and retrieval systems | High; needs GPU infrastructure and expertise |
| Flexibility | Can switch LLMs easily | Model-specific; may require retraining for new LLMs |
Advantages of RAG
RAG shines when you need flexibility, currency, and cost-efficiency. Here are its key benefits:
1. Up-to-Date Information Without Retraining
RAG retrieves the latest data on demand, making it ideal for dynamic domains like eCommerce where prices, inventory, and product details change constantly. You never need to retrain the model, just update your knowledge base.
2. Reduced Hallucinations
By grounding responses in factual, retrieved documents, RAG dramatically reduces the risk of the model fabricating information. This is especially critical in high-stakes domains like customer support, healthcare, or finance.
3. Cost-Effective
RAG avoids the massive computational expense of retraining an LLM. There’s no need for GPU clusters, extended training cycles, or deep ML expertise. Setup costs are lower, and you pay primarily for runtime infrastructure.
4. Seamless Model Switching
If you want to upgrade from GPT-5 to Claude or Mistral, RAG systems can adapt easily. Fine-tuned models, on the other hand, may require you to redo the entire training process with the new model.
5. Works Well with Smaller Models
RAG allows even moderately sized LLMs to punch above their weight by offloading the knowledge burden to external retrieval systems. This democratizes advanced AI capabilities without massive hardware investment.
Enterprises deploying optimized RAG systems in 2025 are reporting 25-40% productivity gains and 60-80% cost reductions in knowledge-intensive workflows
Disadvantages of RAG
However, RAG isn’t a silver bullet:
1. Dependency on Data Quality
Your system is only as good as the data it retrieves. Outdated, irrelevant, or poorly curated documents will produce poor answers. Maintaining high-quality, well-indexed knowledge bases requires ongoing effort.
2. Increased System Complexity
RAG systems have many moving parts—retrievers, generators, indexing pipelines, and vector stores. This modularity creates multiple failure points and demands interdisciplinary expertise in information retrieval, NLP, and system engineering.
3. Higher Latency
The retrieval step adds computational overhead, which can be problematic in latency-sensitive applications. While often acceptable, it’s not ideal for real-time systems where milliseconds matter.
4. Limited Generalization Across Tasks
RAG answers are heavily skewed toward the data retrieved. It doesn’t perform well when tasks require connecting knowledge across multiple domains or generalizing patterns beyond what’s in the knowledge base.
5. Higher Infrastructure and Operational Costs at Scale
While cheaper than fine-tuning upfront, RAG can become expensive at scale. Maintaining fast retrieval systems, embedding generation, vector database management, and high-performance storage all add up, especially under heavy query loads.
Advantages of Fine-Tuning
RAG is usually a more preferred solution for most common use-cases. However, Fine-tuning offers powerful benefits for the right use cases
1. Superior Domain Expertise
A fine-tuned model deeply understands your domain’s terminology, patterns, and nuances. It can provide insights and answers that a generic model never could, without needing external context.
2. Full Control Over Behavior, Style, and Tone
Fine-tuning lets you shape exactly how your model responds—its tone, format, reasoning style, and even potential biases. This is invaluable for brand consistency or highly specialized applications.
3.Fast Inference Without Latency Penalties
Once fine-tuned, your model responds quickly without any retrieval overhead. This is essential for latency-critical applications like real-time customer support or trading systems.
4. No External Data Dependencies
Fine-tuned models operate independently. You don’t rely on external databases, search systems, or third-party services—everything the model needs is in its weights.
5. Better Performance on Complex, Specialized Tasks
In highly specialized domains (medicine, law, finance), fine-tuned models often outperform RAG systems because they’ve internalized domain-specific reasoning patterns.
Disadvantages of Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning a model is considered as more robust solution. However, it is also very challenging, resource intensive and costly
1. Substantial Upfront Costs
GPU clusters, cloud compute, and training cycles often cost tens of thousands dollars. Fine-tuning a 7B model on AWS SageMaker:~$13$+ for 10 short sessions (~50 min each on ml.g5.2xlarge). Pre-training from scratch could cost $50k–$100k+ in total
2. Long Training Times and Iteration Cycles
Each training run takes hours to days, depending on model size and dataset complexity. Debugging and optimization requires multiple iterations, multiplying your costs and time-to-value.
3. High Technical Complexity
You need experienced ML engineers to handle infrastructure setup, hyperparameter tuning, validation strategies, and deployment. Mistakes like overfitting can force you to start over.
4. Data Becomes Stale
Fine-tuned models are frozen snapshots of training data. As information changes (prices, policies, product details), your model becomes outdated and requires expensive retraining.
5. Limited Portability Across Models
Fine-tuning is model-specific. If you want to upgrade to a newer or better model, you’ll need to redo the entire fine-tuning process there’s no straightforward way to transfer your customizations.
Decision Framework: When to Use Each
Choose RAG When:
- Data changes frequently: Your knowledge base is dynamic (prices, inventory, policies, news, regulatory updates).
- You need current information: The model must provide up-to-date, factually accurate responses.
- You’re budget-conscious: You lack resources for GPU infrastructure and extended training.
- You need flexibility: You want to try different LLMs without retraining.
- Your tasks are broad: Queries are diverse and don’t follow predictable patterns.
- Examples: eCommerce product recommendations, real-time customer support, knowledge-based Q&A, help desk automation.
Choose Fine-Tuning When:
- You need domain mastery: Your model must understand specialized terminology and reasoning (medicine, law, finance).
- Your data is stable: Information doesn’t change frequently or update daily.
- You’re optimizing for speed: Low latency is critical; you can’t afford retrieval overhead.
- You have consistent, predictable tasks: Your queries follow patterns the model can learn.
- You have resources: You have engineering expertise and budget for GPU infrastructure.
- You need style control: You require precise control over tone, format, and behavior.
- Examples: Medical diagnosis assistants, legal contract analysis, custom code generation, brand-specific customer interactions.
The Hybrid Approach: RAFT (Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning)
The best approach often isn’t binary—it’s RAFT (Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning), which combines both techniques.
How RAFT Works
RAFT trains your model on domain-specific data while teaching it how to use retrieved information effectively. During training, each example includes:
- A question
- Retrieved documents (some relevant, some irrelevant)
- The correct answer
The model learns to distinguish signal from noise in retrieved content—essentially practicing “open-book exams” in your domain.
Why RAFT Outperforms
A pure RAG system might pull raw data without deep insight. A fine-tuned model might miss real-time updates. RAFT combines the benefits:
- Deep domain knowledge: Like fine-tuning, the model internalizes key patterns.
- Current, accurate information: Like RAG, it leverages external sources.
- Noise filtering: The model learns which retrieved information to trust and use.
- Reduced hallucinations: The model is trained to cite and properly integrate external data.
This is particularly powerful for eCommerce agents, legal assistants, and other domains requiring both expertise and real-time data.
Practical Application of all three Approachs
Let’s take an example of eCommerce solutions, here’s how to apply these concepts:
RAG is ideal for:
- Dynamic product information (prices, availability, specs)
- Real-time inventory queries
- Personalized product recommendations
- Current promotions and offers
- Live customer support with up-to-date policies
Fine-tuning helps with:
- Understanding domain-specific product attributes
- Consistent brand tone and customer interaction style
- Complex product comparisons and recommendations
- Quick response times for common queries
RAFT is best for:
- Your eCommerce agent: Train it on your product taxonomy and customer interaction patterns but augment it with real-time inventory and pricing data.
- Customer support: Fine-tune on your brand’s communication style while retrieving current policies and product details.
Cost Considerations
RAG costs primarily involve runtime infrastructure: vector databases, embedding models, retrieval systems, and API calls.
Fine-tuning costs involve both setup (e.g., data preparation, instance provisioning) and ongoing operations (e.g., hosting for inference). Full fine-tuning of a 7B model typically costs $10–$50 in one-time compute for a single run on AWS SageMaker (e.g., 4–8 hours on ml.g5.2xlarge at ~$1.32–$1.515/hour), plus $100–$500 in initial setup for data storage and processing. Ongoing GPU hosting for inference adds ~$950+/month (e.g., 24/7 on a single L40S or A10G instance). Smaller models or parameter-efficient techniques like LoRA/QLoRA can reduce these costs by 80–95% through lower compute and storage needs
RAFT sits in the middle: you’ll invest in fine-tuning setup but gain long-term efficiency by reducing reliance on expensive retrieval queries.
If you observe technically RAG and fine-tuning are complementary approaches, not competitors.
RAG excels at flexibility, currency, and cost-efficiency perfect for rapidly changing domains like eCommerce. Fine-tuning delivers deep domain expertise and performance guarantees when you have stable, specialized tasks and sufficient resources.
The most sophisticated AI systems especially those handling real-time, complex domains increasingly adopt RAFT, leveraging both techniques to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy with up-to-date information.
The choice ultimately depends on your specific constraints How dynamic is your data? How much latency can you tolerate? What’s your budget? How specialized does the model need to be? Answer these questions, and you’ll know which path or hybrid of paths is right for your use or your use case.
Would you like to share this article?
All Categories
Latest Post
- The Propagation Penalty: Bypassing React Context Re-renders via useSyncExternalStore
- The Memory Leak in the Loop: Optimizing Custom State Reducers in LangGraph
- The Reservation Tax : Mitigating MSI Latency in High-Velocity Magento Checkouts
- Mitigating Crawl Budget Bleed: Detecting Faceted Navigation Traps via Python Generators
- The Catch-Up Tax: Preventing Page Cache Eviction during Kafka Historical Reads